One of the aspects that can be taken to enhance the performance of a telescope, It is linked to the undesired phenomenon of scattered light, due to reflection of the radiation that comes from external sources by the surfaces that precede the telescope detector (or eyepiece), which are characterized by a certain surface roughness (from which it derives the diffuse reflection).
The baffles are devices that allow you to reduce disturbances due to direct illumination sources, or diffuse from the inner surfaces of the telescope, that they tend to decrease the contrast in images or even to cause the so-called ghost (ghosting).
Generally in all telescopes, for groped to reduce the side effects of these disorders, It blackens the inside of the tube with black low reflective paints, so that the radiation reflected from the tube is minimal. In addition to this, however,, you can enter septa (a circular crown walls) which have the purpose of intercepting the 'any light reflected or scattered from the tube, shielding it the primary mirror, in a sense, as you do with your hand on your forehead when you want to shelter from sunlight.
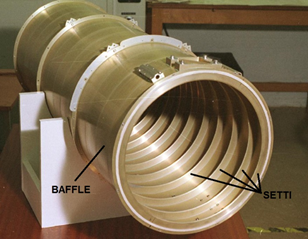
These devices are absolutely paramount in telescopes and optical rooms of the space probes, as well as protecting the sensor from interference sources, due to the sun or to the black body radiation of the planets, alche allow a first passive thermal control of the instrument. They are almost always present in refractors or good quality spotlight, but almost never used in Dobsonian. In fact, for people used to observe very dark skies, the baffles are not essential, because they are missing the main bright interference sources (sole, luna, artificial lights etc.), but for all those who are often observe in sub-urban skies where artificial lights can pollute the image quality, or for those who also observed double stars or objects with the presence of the moon in the sky, then this device can significantly improve the performance of your telescope.
As mentioned earlier, the baffles inside the telescope must be positioned so as to prevent at least the first direct reflection toward the mirror from any part of a surface portion of the inner tube. Baffle well constructed and designed, They may force the light to having to make several reflections before they can reach the primary mirror, thus reducing the intensity of scattered radiation at each reflection. Anyway for amateur applications the elimination of the first direct reflection toward the mirror, is more than enough to raise the quality of the observed image.
EXAMPLE FOR A TELESCOPE NEWTONIAN
- minimum height of the pipe Determination.
N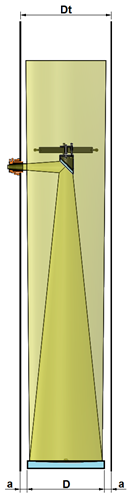 ell'immagine side is represented as a Newtonian telescope scheme, in which we can distinguish, the primary mirror diameter "D", the secondary mirror, the focuser, the inner wall of the diameter of the telescope tube "Dt" and the light cone which opens towards the sky at an angle equal to the own instrument field of view (on one side) and a with a certain size of the illuminated field (on the other). With "a" means the space between the edge of the mirror and the tube wall.
ell'immagine side is represented as a Newtonian telescope scheme, in which we can distinguish, the primary mirror diameter "D", the secondary mirror, the focuser, the inner wall of the diameter of the telescope tube "Dt" and the light cone which opens towards the sky at an angle equal to the own instrument field of view (on one side) and a with a certain size of the illuminated field (on the other). With "a" means the space between the edge of the mirror and the tube wall.
Once you have this data available, you can start by determining which is the minimum necessary length of the tube.
The most obvious criterion is to do it a little higher attachment points of the secondary spider, but this is a hasty solution and not optimal. A better criterion, it is cut to a length such, that no light can get directly into the illuminated field in the focal plane.
To determine this fee, we must draw a line from the lower end part of the illuminated field up to the upper edge, and the innermost telescope, the focuser barrel. Prolonging this line until it meets the inner wall of the telescope from the opposite side, It obtains the minimum altitude at which to end the tube. In fact, every other line departing from an altitude higher than the minimum newfound, not be able to enter the field of light telescope, as incoccerebbe before the barrel of the focuser. In the case of a closed tube, the mirror line to this, that descends in the direction of the primary, it does not matter, in that the tube or the eventual black cloth (in un dobson) shield the rays coming from this area.
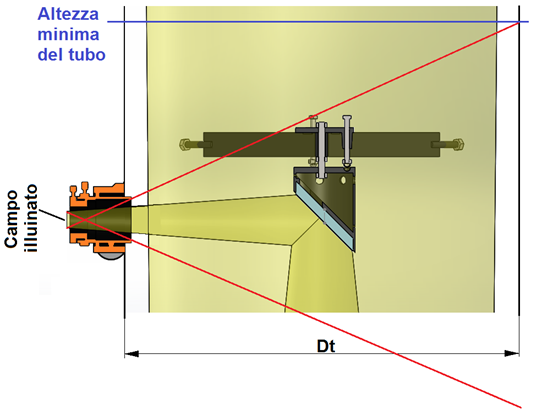
If in your telescope is not it the tube, nor a towel around the reticular structure, it is good to put a lens hood that completely covers the area between the two red lines drawn over (as you can see in this image).

If the hose is too short, then with a height less than the minimum, as often it happens when the selection criterion is to do so terminate just above the spider attachment points, it happens that any light source, artificial and not, that is within the cone outlined in red, image below, It would be able to get straight on the photo sensor or the eyepiece significantly degrading images.
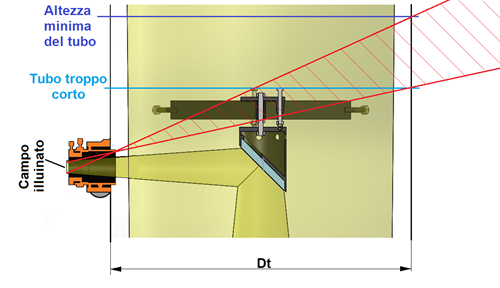
For a Dobsonian Telescope, generally the rule is to minimize the masses and dimensions, thing that induces cells to realize for the very thin secondary, and not able to screen out unwanted light. In this remedy, many amateurs are constructed of removable cylindrical lens hood, to be placed on top of the telescope, who have the dual screen capabilities against external light and protection against fogging and condensation on the secondary.
An example is that described in this article Giulio.